The Gut-Skin Connection: Small Intestinal Bacteria and Rosacea
The small intestine plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption and immune regulation. However, an imbalance in its bacterial population, known as Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO), has been linked to rosacea. SIBO occurs when bacteria that are typically confined to the colon proliferate in the small intestine, leading to inflammation, digestive disturbances, and skin conditions like rosacea.
Key bacteria and microbes linked to SIBO and rosacea include:
-
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori): Known for causing gastric ulcers, H. pylori can alter gut motility and trigger inflammatory pathways that exacerbate rosacea.
-
Methanogenic archaea: These microbes produce methane gas, which slows gut transit and may contribute to bloating, a common SIBO symptom associated with rosacea.
-
Clostridium and Escherichia coli (E. coli): These bacteria release endotoxins that disrupt the gut lining, potentially increasing systemic inflammation and triggering skin flare-ups.
-
Bacteroides: While a normal part of the gut microbiota, an overgrowth in the small intestine can produce metabolites that aggravate rosacea symptoms.
Steps to Combat Small Intestinal Bacteria and Manage Rosacea
Addressing the bacterial imbalance in the small intestine can significantly improve rosacea symptoms. Here are some practical steps:
1. Get Tested for SIBO
If you suspect a link between your gut health and rosacea, consult a healthcare professional to test for SIBO. The hydrogen-methane breath test is a non-invasive way to detect bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
2. Adopt a Gut-Friendly Diet
Diet plays a significant role in managing gut bacteria and reducing inflammation. Consider the following dietary strategies:
-
Low-FODMAP diet: Reduce fermentable sugars that feed harmful bacteria.
-
Anti-inflammatory foods: Include fatty fish, leafy greens, and berries to help calm inflammation.
-
Probiotic-rich foods: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can restore healthy gut flora.
-
Avoid triggers: Steer clear of spicy foods, alcohol, and high-sugar items, which can exacerbate rosacea.
3. Targeted Antibiotic or Herbal Therapy
For confirmed SIBO cases, targeted treatments can help:
-
Antibiotics: Rifaximin or metronidazole are commonly prescribed to reduce bacterial overgrowth.
-
Herbal antimicrobials: Oregano oil, berberine, and garlic extract can be effective natural alternatives.
4. Support Gut Health with Supplements
-
Probiotics: Strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium breve may improve gut health and reduce inflammation.
-
Digestive enzymes: Help break down food more efficiently and reduce bacterial fermentation.
-
Zinc carnosine: Supports gut lining integrity and may mitigate inflammation linked to SIBO.
5. Practice Stress Management
Stress can worsen both gut health and rosacea symptoms. Incorporate relaxation techniques like mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your routine.
Skincare Tips to Complement Your Gut Health Efforts
While addressing gut health is critical, pairing it with gentle skincare can enhance your results:
-
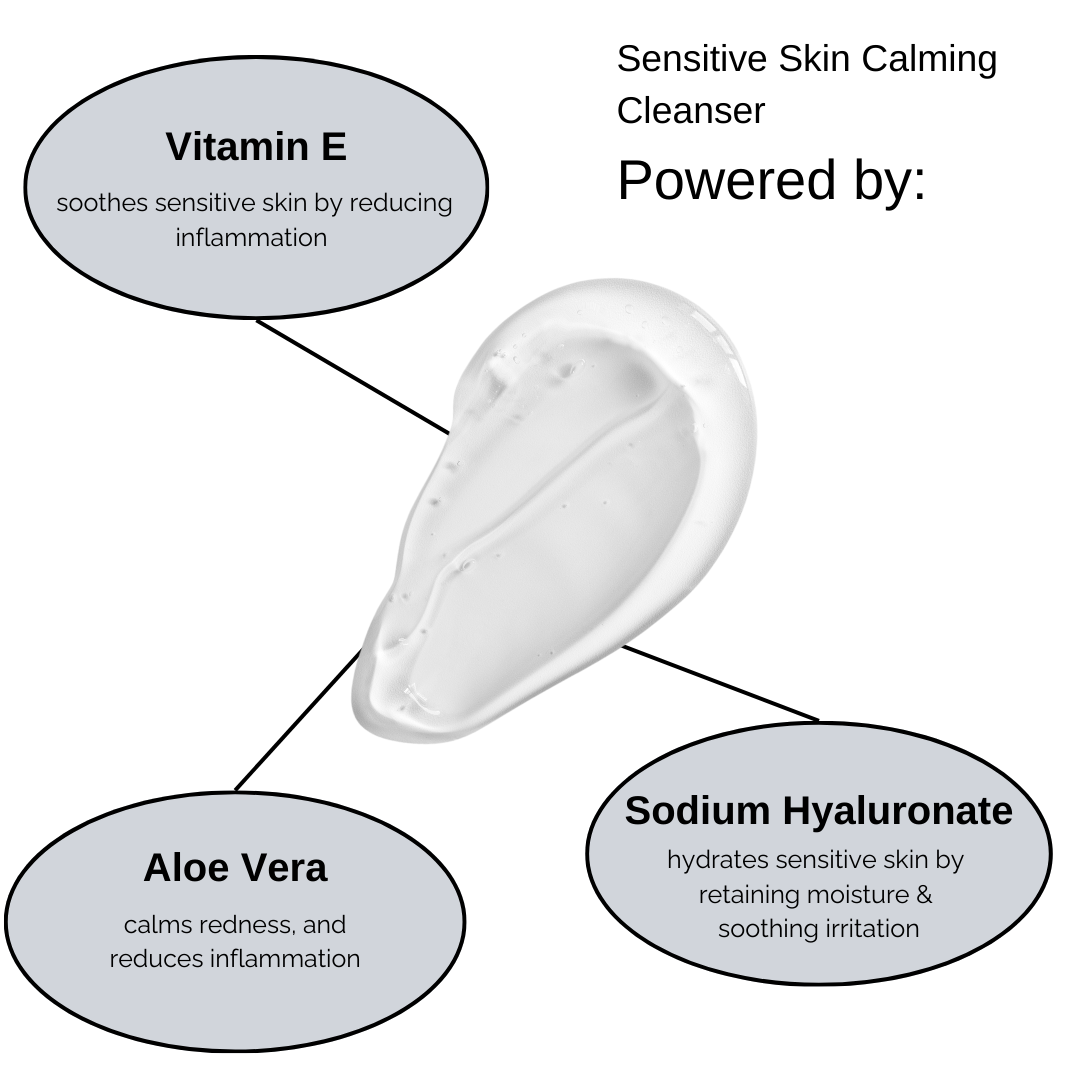
Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic skincare products like RUDDI - we have three incredible products that are rosacea-friendly
-
Apply sunscreen daily to protect sensitive skin.
-
Avoid harsh exfoliants and opt for soothing ingredients like aloe vera and niacinamide.
Conclusion
The link between small intestinal bacteria and rosacea underscores the importance of a holistic approach to managing this condition. By addressing gut health through diet, targeted treatments, and stress management, you can tame your rosacea and achieve healthier skin. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your unique needs.